Cloud service design
Service design is aimed at designing what to offer users through a service catalog. At its most basic, a service catalog is a listing of services from which a user can choose, thus initiating the cloud service provisioning process. When designing a service catalog, it is helpful to identify your cloud users to determine their needs. Potential users to consider while designing critical services offerings include:
- The development team of software engineers
- R&D groups (for example, those engaged in scientific research)
- The application team in charge of building and maintaining internal applications
The challenge of service design is that there is a natural tension among users, who want the ability to completely customize their offerings, and the IT group, which has to maintain tight controls on the services in the environment.
The role of the service catalog is to bridge that gap. The service catalog enables IT to define the areas of configuration and choice that users can select, according to their role. Users then feel some measure of customizability of their cloud services.
The following attributes are often defined in the service catalog:
- Resource configurations – including CPU, memory, and storage allocations
- Operating systems
- Middleware stacks
- Applications offered
- Networking options – for both simple network configuration and multi-tenancy support
- Compliance packages
- Monitoring tools
- Service levels
- Prices associated with each component, if desired
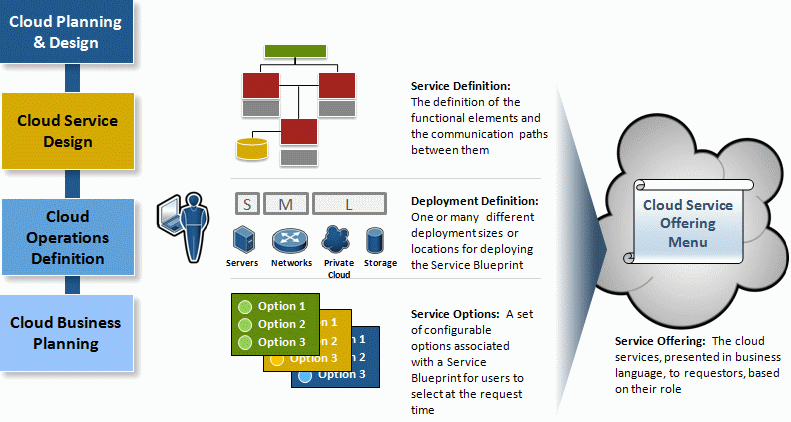
Inherent in this list is the ability to define multi-tier and single-tier application stacks, differing deployment alternatives for each based on size and service tier, and all the configuration options a user might require. These elements are defined as individual Service Blueprints within the BMC Cloud Lifecycle Management solution. Once defined functionally, they are then characterized in business language as service offerings, which are stored in the service catalog. It is from these offerings that end users select their cloud services.
Cloud service design overview diagram
IT can choose which cloud services to offer to users and how customizable those services will be. At one extreme, users can be offered a choice between only two or three non-customizable full-stack configurations. On the other extreme, users can be offered an extensive set of choices for each component, enabling them to fully customize their stack. A common middle-ground approach is for IT to determine which broad offerings should be presented, which elements should be optional and which required (like compliance or monitoring), and which users will be presented with which options.
Beyond the contents of the service catalog, service design also includes the design of the workflows that support each provisioning process. For many, the workflow will be an automated series of approvals. However, for some, human approval might be required, due to the sensitivity or scale of the request. Designing these workflows is critical to service design.
To address the needs of cloud service design, you should:
- Design internal and external cloud services
- Define service tiers and service levels
- Create a "bill of materials" for each service
Comments
Log in or register to comment.