Performing the initial configuration snapshot
BMC Network Automation is configured by default to back up 20 devices concurrently. BMC recommends verifying that the BMC Network Automation system is correctly configured by first testing a Snapshot span action on a few representative devices. After completing the verification, submit a Snapshot span action for a larger set of devices (for example, group, default realm, or filtered set of devices).
Before you begin
Verify your setup according to the following guidelines:
- Ensure that any firewalls between the server and managed device are not blocking file transfer service application ports. BMC Network Automation initiates file transfer from the device for Snapshot, Deploy to Stored, Deploy to Active and Deploy or Snapshot OS Image span actions. Tunneling is available for taking a snapshot if you cannot open a file transfer port on the firewall.
- When installing BMC Network Automation on a Microsoft Windows server that uses a firewall, ensure appropriate file transfer service application ports (for example, TFTP/FTP/SCP) are not blocked. For instructions on how to unblock ports, see Unblocking ports.
- Ensure that the appropriate file transfer services (for example, TFTP, FTP, SCP) are running on the server. For instructions on installing and configuring these services for your operating system see Installing optional components on Windows or Installing optional components on Linux.
Note that for Windows, BMC Network Automation automatically installs and starts a TFTP server, but the FTP and SCP services must be installed separately. - Ensure that you have configured the TFTP/FTP/SCP services for the Local (default) and any remote Device Agents under Admin > Device Agents.
- Define the device security profiles (DSP) needed to access your network devices. As required, ensure the DSP account is configured on your RADIUS or TACACS+ server. The DSP account must have rights to take a snapshot of the full configuration.
- Under Admin > System Parameters, verify that the device access timeout values are appropriate for your WAN performance.
To test the Snapshot span action on a few devices (example)
The following is an example of a configuration snapshot on a few representative devices using TFTP on a Cisco IOS router:
- Use Telnet to connect to the device (router).
- Log on and go to Enable mode.
- Enter copy running-config tftp.
- Enter the BMC Network Automation IP address when prompted for the address of the remote host.
- Enter temp.tmp when prompted for destination file name.
If the snapshot fails, the Job transcript shows where the error occurred. To diagnose the problem manually attempt the login using the assigned DSP credentials and access mode (for example, telnet). Then try the configuration file transfer.
If the previous test fails, the server might be behind a NAT device or firewall. Find what IP address the router uses to address the server. This is the address that gets translated to the Server IP Address by the NAT device. Whatever that address is, enter it in the NAT Address field for the device record. In other words, edit the device record and just under where you specified Access Mode, File Transfer Mode, and DSP, you see the NAT Address field.
To schedule a large Snapshot
- Configure the device interface parameters.
For new devices, BMC Network Automation assigns Auto as the default DSP, Access Mode and File Transfer Mode. If your environment uses a single DSP, Access Mode (for example, SSH) and File Transfer Mode (for example, FTP), use the mass Edit option on the device list to set all or a filtered set of devices to the same values.
If you select to use the Auto feature, here is how it works:- DSP: Tries DSPs by assigned priority order until one works.
- Access Mode: Tries the most secure (for example, SSH2) to least secure (for example, Telnet), combined with the TCP port from the global.properties.imported file and with the well-known port, until one combination works.
- File Transfer Mode: Tries the most secure (for example, SCP) to least secure (TFTP) supported file transfer mode until one works.
- In all cases, BMC Network Automation assigns the working value to the device's record.
- Use the Job Details report to audit by device the snapshot success or failure status. The device transcript shows where the snapshot failed.
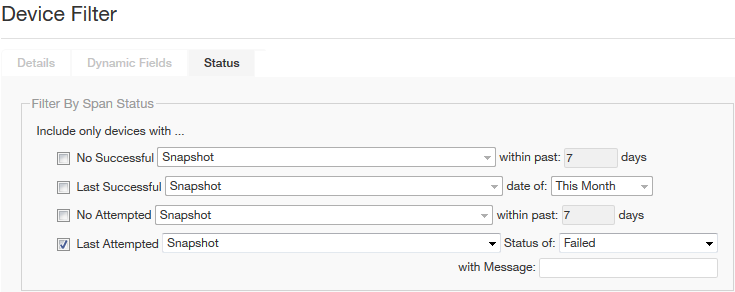
- Resolve the access problems and submit a Snapshot span action with the filter set to only take a snapshot of the devices where the last snapshot failed, as shown in the following figure. (Only the Filter By Span Status pane of the Status tab is shown in this figure. For more information see Managing devices.)
Comments
Log in or register to comment.